How it
works
Every Patient is Unique
Patients have a variety of obstacles to overcome when it comes to blood extraction - fear of
needles, pain, contamination, blood clotting, and other adverse effects.
HERE COMES THE
REVOLUTION...

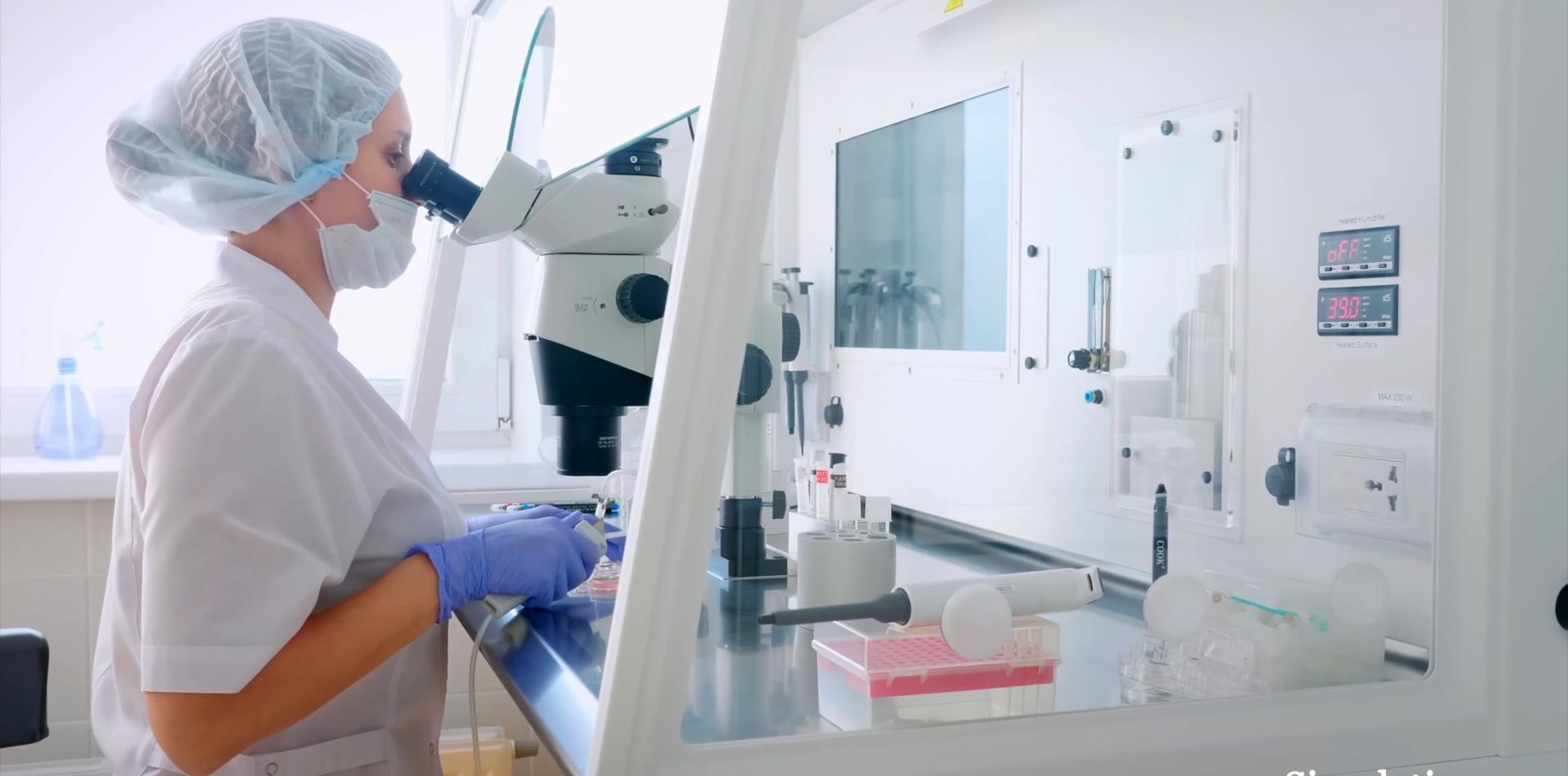
To obtain those 4 values, we utilize two medical hardware devices produced by
leaders in the healthcare industry.
4 key inputs
- partial pressure of carbon dioxide/tcpCO2
- partial pressure of oxygen/tcpO2
- total hemoglobin/SpHb
- body temperature
Breakthrough
Software
Gathered results are sent to our system for the next step of processing. PK Software from DBC leverages a unique algorithm, allowing it to generate an additional 18 blood values that are monitored in real-time.
Classic method
VS. DBC
Classic method
In order to reduce turnaround time, some hospitals have adopted an outdated cart system, whereby a laboratory technician is placed near hospital rooms that require frequent blood-gas tests. Such critical care units include emergency rooms, operation theaters, and intensive care units.
DBC method
A turnaround time of 5-15 minutes still exists in these systems. Moreover, the cost of the unit is based on the volume of tests performed. Maintenance of these units is expensive and requires a skilled technician. Apart from this, additional space in the hospital is very valuable.
| Classic method | DBC | |
| Biological waste |  |
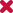 |
| Skilled personnel |  |
 |
| Blood transmitted diseases |  |
 |
| Need of a needle |  |
 |
| Pain and bruises |  |
 |
| Time consuming |  |
 |
| Real time sharing |  |
 |
| Cost efficiency |  |
 |
Potentional use
of DBC technology

Hospitals
INTENSIVE CARE UNITS/EMERGENCY ROOMS.
DBC technology saves time and energy in life-threatening situations when doctors can't afford to wait for a full medical blood panel. The software also minimizes risks for patients.

Ambulance
Thanks to DBC software, EMT personnel can get patient blood panels immediately. Then, information gained in the field can be provided to doctors at the hospital, allowing them to start surgery or treatment immediately.

Government
Real-time monitoring of blood values has potential applications in drug development/testing, as well as to assess the health conditions of athletes, pilots, astronauts, and military personnel in combat situations.





